Link ad
Followers
Tuesday, February 23, 2021
E-magazine
Here, there are many links of various type of magazine in the given below page. so you click on magazine whatever you want to read.
Sunday, February 21, 2021
Friday, January 29, 2021
Web links of e-Content & Learning Material (Class-VIII)
This is the Web links of e-Content & Learning Material for class VIII prepared by NVS and DIKSHA. if you want to see and read the study materials of all subjects, you can click on particular subject link given.
Monday, January 25, 2021
Saturday, January 23, 2021
Monday, January 11, 2021
Conservation of plants and animals
• Deforestation and its causes:
The variety of plants and animals existing on earth are essential for the well being and survival of mankind. Today a major threat to survival of mankind is deforestation.
Deforestation means clearing of forests and using that land for other purposes, i.e. for industries set up or making building for rehabitation.
The causes of deforestation may be:
- Procuring land for cultivation.
- Building houses and factories.
- Making furniture, using wood as fuel and
- Natural causes such forest fires and draughts.
- Deforestation causes increase of atmospheric temperature due to increase in concentration of carbon dioxide leading to global warming, Severe draughts and floods.
- Deforestation changes the nature of soil, water holding capacity and soil erosion. Gradually, the fertile land gets converted into deserts. It is called desertification.
Deforestation causes the destruction of habitat of wildlife, its survival becomes difficult.
• Biosphere: The part of the earth in which living organisms exist or that supports life is known as biosphere.
• Biodiversity or Biological diversity: It refers to the variety or organisms existing on the earth. Their interrelationships and their relationship with the environment. It includes variety of plants, animals and microorganisms.
•
Flora and Fauna: The plants found
in a particular area are termed as flora area. The animals found in a
particular area are termed as fauna of that
area.
• Endemic Species: Those species of plants arid animals which are found exclusively in a particular area are called endemic species to a zone, a state or a country. For example, sal and wild mango endemic flora of the Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve. Animals such as Bison, Indian giant squirrel and fly squirrel are endemic fauna of this area.
• Species: A group of population or populations whose members have common characteristics and are capable of interbreeding among themselves to produce fertile off-springs. Normally, members of a species breed amongst themselves and not with members of other species
• National parks, sanctuaries and biospheres reserves are maintained to conserve forests and wildlife.
• Biosphere Reserve: AA larger protected area meant for conservation of biodiversity and culture of that area is called Biosphere Reserve. A biosphere may consists of other protected areas such as National Parks and Sanctuaries. For example, Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve consists of one National Park called Satpura and two Wildlife Sanctuaries known as Bori and Pachmarhi.
•
Wildlife
Sanctuaries: These are the protected areas which provide protection and suitable
living conditions to wild animals. Sanctuaries are places
where killing (poaching) or capturing of animals is strictly prohibited.
A sanctuary may be a reserved natural area meant for the
preservation and development of threatened/endangered species. For example,
there is the Kaziranga Wildlife Sanctuary for Rhinoceros in Assam.
•
National Park: A national park
reserve is large and diverse enough to protect
whole set of ecosystem. National Parks preserve flora, fauna, landscape and
historic objects of an area. For example. In the Satpura National Park, Rock
shelters and Rock paintings are also
preserved along with flora and fauna.
•
Endangered
Animals: Animals whose numbers are diminishing to a level that they might face
extinction are known as the endangered animals. For example, dinosaurs became extinct a long time ago.
• Ecosystem: All the living components,
such as plants, animals and microorganisms and non-living components such as
climate, soil, river, deltas etc. constitute an ecosystem. An ecosystem can be
as small as a pond or as big as an ocean or a
forest.
•
Red
Data Book: The source book which keeps a record of all the
endangered animals and plants. There
are different Red Data Books.
•
Migration:
The phenomenon of movement
of a species from its own habitat to some other for a
particular time period every year for a specific purpose like breeding is known
as migration.
• Reuse and
recycling of paper save trees, energy and water.
• Reforestation is
restocking of the destroyed forests by planting new trees.
Sunday, January 10, 2021
Microorganisms and their advantages
CHAPTER –2 Microorganisms
Introduction
Organisms that are so small that they can only be seen through a microscope are called microorganisms or microbes.
The study of microorganisms is known as microbiology.
Most organisms are hardy and can be found in almost any kind of environment – hot desert, polar ice caps, salt water, marsh lands and inside other organisms.
Types of microorganisms:
There are five major groups of microorganism. These are as follows:
1.
Bacteria
2.
Algae
3.
Protozoa
4. Fungi
5. Viruses
Bacteria:
· They are simple living organisms which are found all around us. They are mostly single- celled tiny organisms, but they live together in colonies of millions.
· Bacteria are found in three different shapes:
1.
Rod shaped, called bacilli.
2. Spherical shaped, called cocci.
3. Spiral called spirilla.
Algae:
· Algae are simple plant- like organisms which are usually aquatic in nature.
· They contain a cell wall and chlorophyll and can make their own food by photosynthesis.
· Algae can be unicellular or multicellular.
· Some of the common examples are diatoms, Chlamydomonas, and seaweed. Protozoa:
· These are unicellular microscopic organisms similar to animals that can move about to capture food and are heterotrophic in nature.
· They are mostly aquatic in nature.
· Amoeba, paramecium are some examples of protozoa. Fungi:
· Plant -like organisms that do not contain chlorophyll are called Fungi.
· Fungi may be unicellular (Yeast) or multicellular (Bread mould) and are found in warm and moist places.
· Fungi can be heterotrophic, saprophytic or parasitic in nutrition.
· Examples: Yeast, Rhizopus (Bread mould), mushrooms, puffballs. Viruses:
· Viruses are smaller than any known cell.
·
Viruses can only be seen with electron microscope.
· Viruses can reproduce only
inside the bodies
of other organisms, which mean they need
a host.
· A virus is like a non- living thing outside the body of other organisms. Therefore, it is a borderline between a living and a non- living thing.
USEFUL MICROORGANISMS
Microorganisms
are useful in the following ways:
·
In making medicines and vaccines
·
In
agriculture
· In cleaning the environment
Food and beverage industry:
· Bacteria help us in making certain foods. Lactobacillus is a bacterium that sours milk and is used to makes curd from milk.
· Many fungi like Mushrooms and morels are edible which are rich
· Yeast is commonly employed in preparing food items like bread, cakes, idli, dosa, dhokla etc.
· Yeast is also used in breweries for making wines by the process of fermentation.
Making medicines and vaccines:
· Bacteria and fungi are used to make medicines called antibiotics.
· The first antibiotic, penicillin was discovered by Alexander Flemming using the fungus penicillium.
· Some common antibiotics are streptomycin and terramycin.
· Microbes are used to make vaccines. Vaccines are weakened or dead germs introduced into the body. They offer protection against diseases like tuberculosis, polio etc. by producing anti- bodies.
· Bacteria and Yeast are used in making vitamin B complex tablets.(Escherichia coli survive in our intestine produces B-12)
· The human hormonal called insulin can also be obtained from bacteria.
In Agriculture:
· Some bacteria like Rhizobium, blue green algae like Nostoc, live in the root nodules of plants such as gram, pea etc. These bacteria absorb the nitrogen of the atmosphere and convert it into nitrate which serves as natural fertilizers for plants, hence, enhancing soil fertility.
In cleaning the
environment:
·
Microbes help to keep
our environment clean
by decomposing dead matter. They decomposed substances are recycled
as these get reused from the soil
by plants.
·
Some bacteria decompose sewage and other waste
in water. This
is nature’s method of keeping
the environment free from pollution.
HARMFUL MICROORGANISMS
· Microorganisms that cause diseases
in human, animals
and plants are called
pathogens or
germs.
·
Germs may enter the
body of living
organisms through air,
contaminated food and water, from an infected
person by direct
or indirect contact
or by a carrier.
·
Diseases that
can spread from
an infected person
to a healthy individual through
air, water or direct
contact are called communicable diseases. Examples: Common cold, chicken pox, AIDS etc.
·
Micro
organisms also cause
diseases in animals
and plants. For examples-
·
Anthrax is a disease
caused by bacterium and affects human
and cattle.
·
A virus causes
the dangerous foot and mouth disease
in cattle.
·
Citrus canker is a bacterial disease that affects
trees of citrus
fruits and is spread by air.
·
Rust of wheat
is
a viral disease
that affects vegetable like bhindi &
spread by insects.
· Malaria is actually caused
by pathogen called
plasmodium (protozoa) which
is transmitted by female Anopheles mosquito.
· Dengue is caused by dengue virus and spread by female Aedes mosquito.
Preventing the
spread of Communicable diseases:
Some simple methods of limiting the spread of communicable diseases are:
·
To keep
the infected person
separated from others
& to advice
his/ her to keep a handkerchief on the nose and mouth while sneezing.
·
To
keep our environment or surrounding clean.
·
Never
let garbage collect
in the neighborhood.
·
Timely vaccination against diseases
should also be taken.
·
To prevent
mosquitoes from breeding
we should not allow water
to collect anywhere in our neighbourhoods.
Food spoilage:
Many bacteria and fungi grow on food items and produce certain toxic substances. This makes the food unfit for consumption. Consuming such food can cause a serious illness called food poisoning.
Food preservation:
· Processing of food to prevent their spoilage and to retain their nutritive value for period is called food preservation.
· Food can be preserved using many methods:-
1. Heating: heating food to a high temperature kills microbes. For example: Milk and water are boiled to kill microbes.
2. Cooling: food can be kept in refrigerator at about 5˚C which delays its spoilage.
3. Canning: canning is done to package or preserve food or drink by putting it in sealed, airtight containers.
4. Salting: Fruit and vegetables can be preserved by using salt and then drying. Salts prevent the growth of microbes.
5. Sweetening: Excess sugar can also works on the same principle as salting. Jams, jellies & squashes are preserved by this method.
6. Dry or dehydration: Dehydration of food remaining water from it. This stops microorganisms from growing as they cannot grow without water.
7. Chemical preservatives: Chemicals like sodium benzoate and sodium meta-bisulphite prevent microbial attack and are often use to preserve jams, sauces & ketchup.
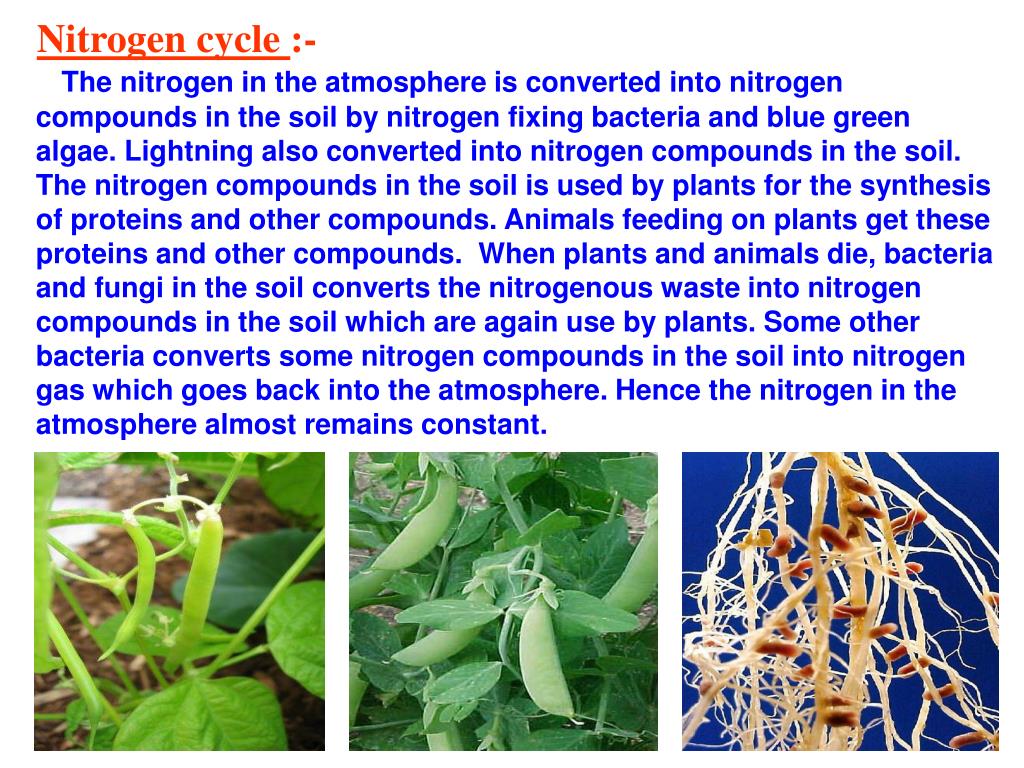
Nitrogen cycle :-
The nitrogen in the atmosphere is converted into nitrogen compounds in the soil by
nitrogen fixing bacteria and blue green algae. Lightning also converted into nitrogen
compounds in the soil. The nitrogen compounds in the soil is used by plants for the synthesis
of proteins and other compounds. Animals feeding on plants get these proteins and other
compounds. When plants and animals die, bacteria and fungi in the soil converts the
nitrogenous waste into nitrogen compounds in the soil which are again use by plants.
Some other bacteria converts some nitrogen compounds in the soil into nitrogen gas which
goes back into the atmosphere. Hence the nitrogen in the atmosphere almost remains constant
feature post
Important questions of biomolecules
BIOMOLECULES QUESTIONS VSA TYPE QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 1. Name polysaccharide which is stored in the liver of animals. 2. Wh...